Read on to learn more about the basics of AI, Excubate’s AI player selection process, and a brief introduction to an example AI manufacturing solution.
Excecutive Summary
Companies collect huge amounts of data on all kinds of business processes. Analyzing this data and turning it into tangible business value is uncertain, complex and time-consuming. A rapidly growing number of artificial intelligence-based software solutions aim to solve this challenge by using intelligent algorithms to analyze data sets, derive insights, and automatically recommend actions. Beneficial use cases can be found along all stages of the value chain; getting started is often easier than it seems. Examples show that ROI can be achieved as early as after just one day.
What is “AI”?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a subfield of computer science that aims to enable machines to replicate human thinking and decision making. This is often achieved with machine learning (ML) algorithms, that continuously learn from datasets. In many cases the current discussion about AI is in fact a discussion about its subfield ML.
In comparison to classical systems (hardcoded and simple rule-based), ML algorithms can learn from existing data to react to previously unknown situations. Example: AI can learn what a person looks like from several existing images and then apply that rule to new images and recognize that person. This is possible due to the ML algorithms’ ability to recognize patterns in data and derive rules and statements from it. ML can be used in situations where large quantities of complex and unstructured data must be analysed and searched for patterns. It is faster and more accurate than human analyses of the same.
The potential use cases for AI are numerous but have yet to be fully understood. Here are some relevant business examples:
- Manufacturing process optimization achieved by sensor-controlled anomaly detection (e.g. prevention of unplanned downtimes, using machine vibration analysis)
- Recruitment improvement by matching talent supply and demand (AI-powered analysis to assess an applicant’s previous work experience and interests and match them with the most suitable job openings)
- Price optimization based on historic and real-time data to predict how customers are likely to react to different pricing and automatically adjust it accordingly (e.g., ML algorithms crawl the web to gather information about competitor prices and trends to adjust own prices while keeping in mind business goals)
- Product & process development, enhanced by design suggestions, consistency checks or predicted product properties for changed parameters
- Automatic lead identification based on similar existing customers or market data, including information on customer intent (e.g., “What will my customer buy next?”)
Realizing tangible value with AI
In many cases, companies are hesitant to introduce investment-intensive technologies – and often wait until best practices appear on the market and risks are foreseeable. However, when it comes to AI, hesitation might lead to a significant loss of opportunity. Experts go as far, as to call AI as an essential building block for the future viability of companies. Within the last two years we observed 5 major challenges, that companies are facing when implementing AI technology:
- Identification of impactful, measurable, and individually fitting use cases, including creation of transparency on their quantified benefits and risks.
- Knowledge about what and how data can be used, data quality, and availability of data relevant to the application area.
- Internal AI technology knowledge and hiring high-in-demand data science teams or training existing personnel.
- Complex and time-intense integration of AI solutions in legacy systems (e.g., SAP).
- Ambiguity of what applications are available on the product and process side, oversupply in emerging solutions, and unclarity in regards of make or buy benefits.
Despite these challenges, AI usage is on the rise. In a 2021 McKinsey study with over 1.800 international companies, 56% of all respondents reported AI adoption in at least one business function. Furthermore, 27% of respondents reported a minimum of 5% EBIT that is attributable to AI.
Today, the benefits of AI outweigh the costs in a wide range of use cases. Using the Digital Value Canvas® (read here more about the methodology) the benefits of AI usage in the example of industrial manufacturing can be mapped as followed:
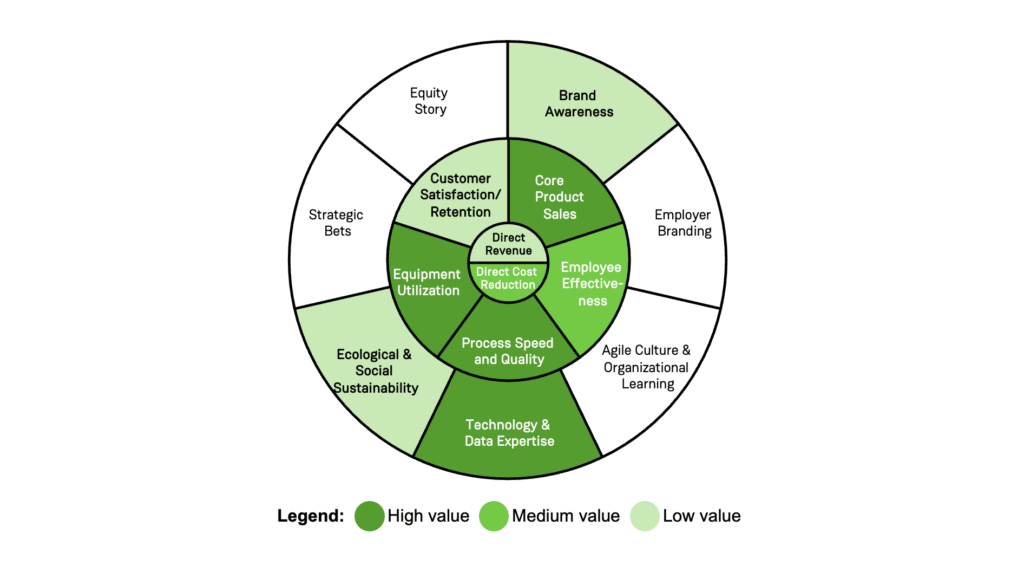
Using Excubate’s Digital Value Canvas©, the potential value impact of AI usage in manufacturing can be assessed.
Based on project experience, main value drivers of AI usage in manufacturing are:
- Core Product Sales: For example, AI-based image processing promises reliable defect detection and higher batch quality. The better addressed customer needs result in increased competitiveness and sales if market demand permits.
- Process Speed & Quality: In general, AI is not subject to performance fluctuations and delivers constant quality and speed. For instance, process models are used to compare as-is with to-be state in real time. In case of deviations, AI systems are able to automatically search for root causes and can trigger process changes.
- Equipment Utilization: Reduced downtime and inefficiencies through predictive maintenance leads to higher lifetime of machines, as well as higher degree of utilization, performance, and quality.
- Technology and Data Expertise: AI adoption enables the step into industry 4.0 and data-driven solutions. The dealing with associated topics creates knowledge spill over effects and sets the foundation for further expansion towards more autonomous productions.
A way to kickstart AI usage: partner-up and find the right solution!
Excubate supports companies in identifying technology use cases, formulating respective strategies, and identifying the right partners. In this article we want to give a short introduction to our standardized, six-step process for strategic (AI) partner selection. It enables a fast understanding of any technology as well as an implementation kickstart.
- If not clear: clarify use case, underlying technology, and initial search scopeg., through ideation workshop, interviews with business units and stakeholders, by derivation from strategic goals etc. Additionally: creation of hypothesis tree (“What do we have to believe in for a solution to be a good fit?”) for later ranking of left solutions
- Research of player long-list: wide-scope research of any solution that falls into the high-level search grid; quantity over quality to ensure to not miss out on any solution
- Definition and application of knock-out criteria: Search for specific criteria that can be used to steam down the longlist e.g., customer focus of solution, industry experience or GDPR conformity of player, …
- Reduction by business stability: Defining revenue and employee amount thresholds to exclude companies with low commercial performance
- Reduction by challenge-solution fit: Identifying business unit challenges, matching them with the solutions of left players, and abandoning of unsuitable solutions
- Forced Ranking through hypothesis tree: Quantification of hypotheses and subsequent evaluation of players based on the extent to which hypotheses were fulfilled
- One Pager Creation for top 5 players: Presentation of top player key facts and numbers; product/solution summary
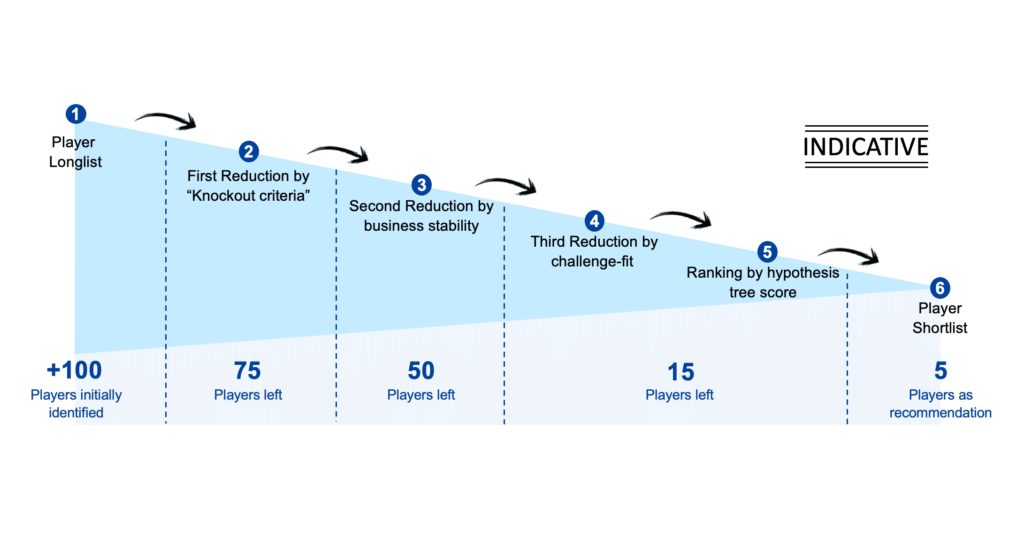
Our process results in a wide market overview and a top 5 player recommendation for each respective use case in scope. It enables our clients to directly engage best fit partners and quickly introduce value-adding solutions to the core business. We directly tackle the most common challenges companies have (as were stated above):
- Identification of use cases: we enable our clients to identify the best fit use cases in their value chain and to ensure tangible business benefits
- Insufficient data quality and availability: we bring clarity in all data requirements and recommend needed action; we support in communicating requirements with respective business units
- Lack of internal knowledge: we bring transparency in the technology, its benefits, respective use cases and the overall solution market
- Integration of AI solutions in legacy systems: we support in selecting solutions that are integrable and pragmatic; we support in defining requirements for overall integration in legacy systems
- Oversupply in emerging solutions: we offer a clear path forward, by providing a selection of top-notch partners and recommendations for a fast and pragmatic implementation
Output example: Best-fit players mapped along client sales value chain (each coming with respective detail one pager)
Solution example: dismiss unplanned machine downtimes by analyzing vibrations
Rotating equipment in manufacturing environments is often subject to issues, such as bearing damage, imbalance faults, cavitations, misalignments, and gearbox faults which often aren’t detected until it’s too late.
These typical problems result in inefficiencies and downtimes which, in general, can lead up to 20% of total production costs and 10% of global production losses. In the automotive sector, for example, average costs of 2.5 million Euro accumulate from just a one-hour outage.
In a past research project, Excubate applied the described research approach and identified a company that can solve such challenges. This particular solution provides AI-powered vibration-based sensors and associated software to avoid unplanned downtime of rotating equipment. The predictive maintenance solution supports early fault detection and thus avoidance of damage, production downtime, and loss of production. Testing of this solution is possible even in just a couple of days. Through a fast sensor installation, subsequent data collection and intelligent analysis, it is possible to detect first anomalies after a couple of days. This can lead in the best case to a return on investment after the first day of solution deployment.




